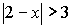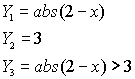Absolute Value
|
Working with Absolute Value (Equations and Inequalities) |
Example 1: Solve:
|
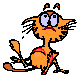  |
|
|
||
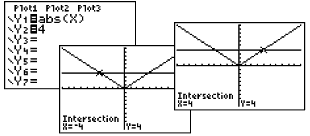
Example 2: Solve:
|
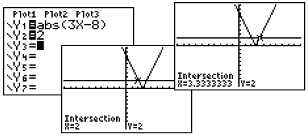 |
| Example 3: Solve:
|
 |
Example 4: Solve: Boolean Check:
Where the inequality is true, y-values on the graph will be a 1. |
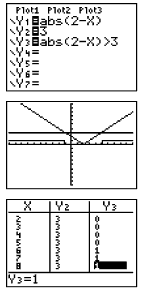
|
|||||
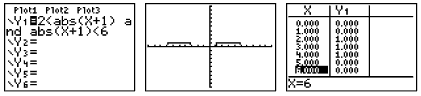
Determine exact cut off points by using the intersection option. Remember that the calculator cannot draw an open or closed circle on the intervals. You will have to determine which circle is needed based upon whether the inequality includes "equal to". Find the endpoints by using the intersect option (2nd TRACE #5 intersect). If you turn off the axes (FORMAT - 2nd ZOOM),
you will be able to see the graphing of the 0's and 1's more clearly.
Notice that the small vertical segment connecting the 0's to the 1's
is simply the calculator being set in "connected" mode.
Change to "dot" mode to remove this segment. |
||||||
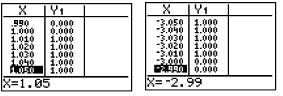
| You "can" enter the inequality directly. Since you will not have the two graphs from which to determine the intersection points, you will need to examine the table to determine the exact value of the open/closed endpoints. |
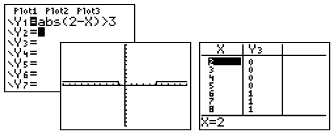 |
| Example 5: Solve: Algebraic solution: 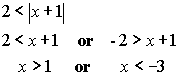 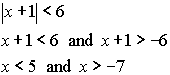 Answer: The values that make the compound inequality true are Calculator solution: (inequality expression is entered using
"and") |
![]()
Finding Your Way Around
TABLE of CONTENTS